What Is the Right Milk for Your CS-Born Child?
Breastfeeding is the best source of nutrition for all children because it provides complete and balanced nutrition perfectly matched to the needs of a growing child. However, if breast milk is not an option, check with your doctor before deciding on an alternative feed for your little one.
Research reveals that the mode of delivery may impact early child development. In turn, the choice you make for your child’s milk product and nutrition support is particularly important. For children born by cesarean, the initial probiotic transfer is bypassed. This may lead to health challenges associated with inadequate nutrition support from maternal probiotics.
Click HERE to learn more about Nutrition Support for CS-born children.
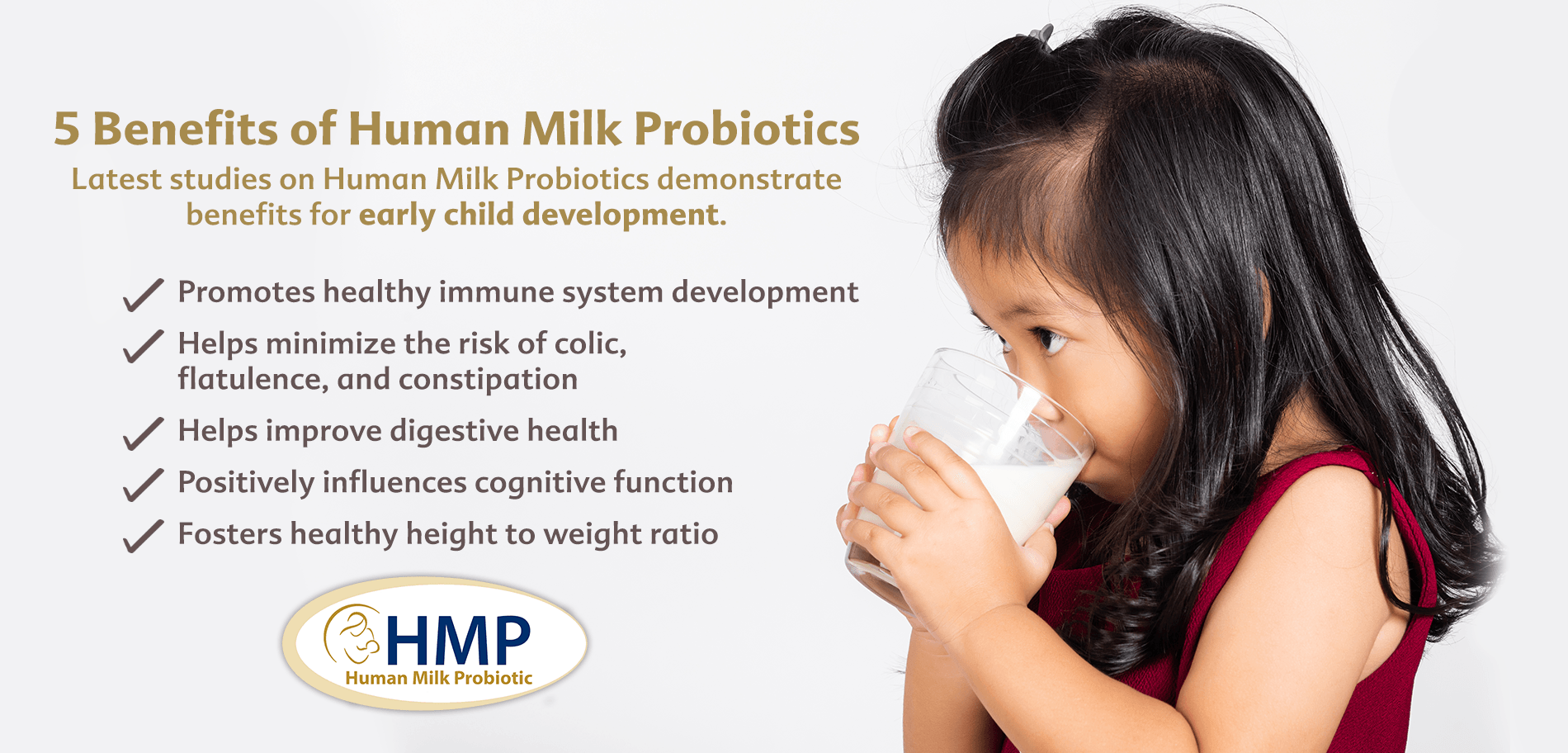
The initial transfer of maternal probiotics from mother to child happens during natural delivery. These maternal probiotics bear multiple benefits that include supporting the early development of the immune system and positively influencing a child’s digestive health to prevent common digestive problems like colic, flatulence, and constipation. More importantly, probiotics play an important role in the early development of cognitive function, memory, and verbal learning.
Keep in mind that your choice of nutrition support for your CS-born child is crucial to their developmental needs. Breast milk is nature’s way of meeting your child’s growing nutritional needs. More importantly, breast milk can correct the absence of initial probiotics in CS-born children because it contains Human Milk Probiotics.
Click HERE to download a list of Evidence-based Benefits of HiPP Organic CS Kindermilk.
What are Human Milk Probiotics?
Probiotics function in different ways and have different survivability rates. Some probiotics do not survive beyond the gastric area and are therefore rendered ineffective. Human Milk Probiotics are “friendly” bacteria that are present in breast milk and have the unique ability to survive the hostile gastric acid and oxygen-rich environment of the stomach.
References:
Dominguez-Bello M, et al. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:11971–11975.
Gil-Campos M, et al. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 is safe and well-tolerated in infants of 1-6 months of age: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacol Res 2012;65:231-238.
Łubiech K, Twarużek M. Lactobacillus Bacteria in Breast Milk. Nutrients 2020;12: 3783.
Maldonado J, et al. Human milk probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 reduces the incidence of gastrointestinal and upper respiratory tract infections in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2012;54:55-61.
Tooley KL. Effects of the Human Gut Microbiota on Cognitive Performance, Brain Structure, and Function: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):3009.
Valdes AM, et al. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018;361:k2179.
Vandenplas Y, et al. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infancy: Impact on the Health of the Infant and Family. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(3):207-216.
Wiertsema SP, et al. The Interplay between the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System in the Context of Infectious Diseases throughout Life and the Role of Nutrition in Optimizing Treatment Strategies. Nutrients. 2021;13(3):886.
Yang I, et al. The Infant Microbiome: Implications for Infant Health and Neurocognitive Development. Nurs Res 2016;65:76-88.